Concept
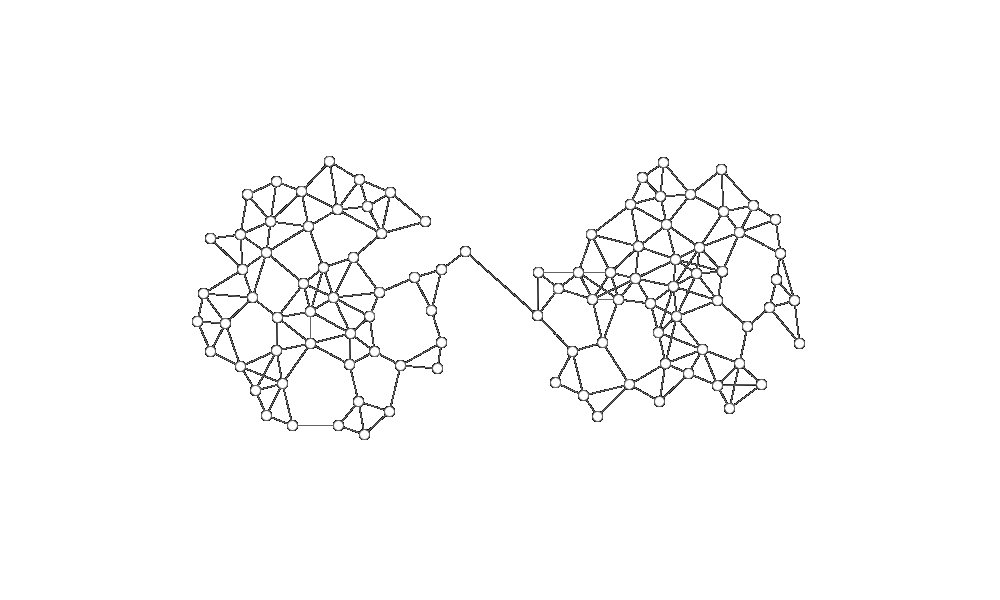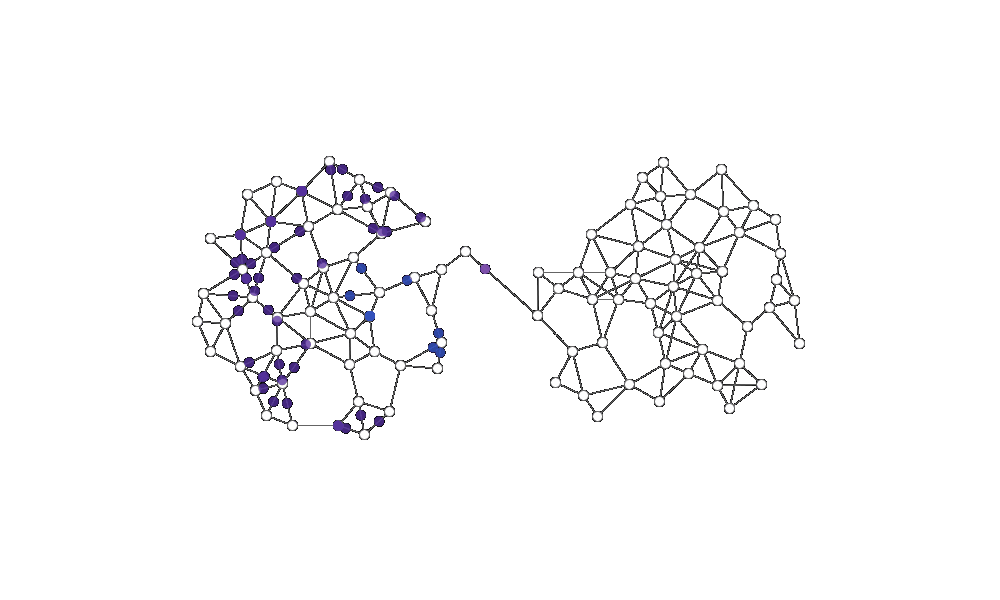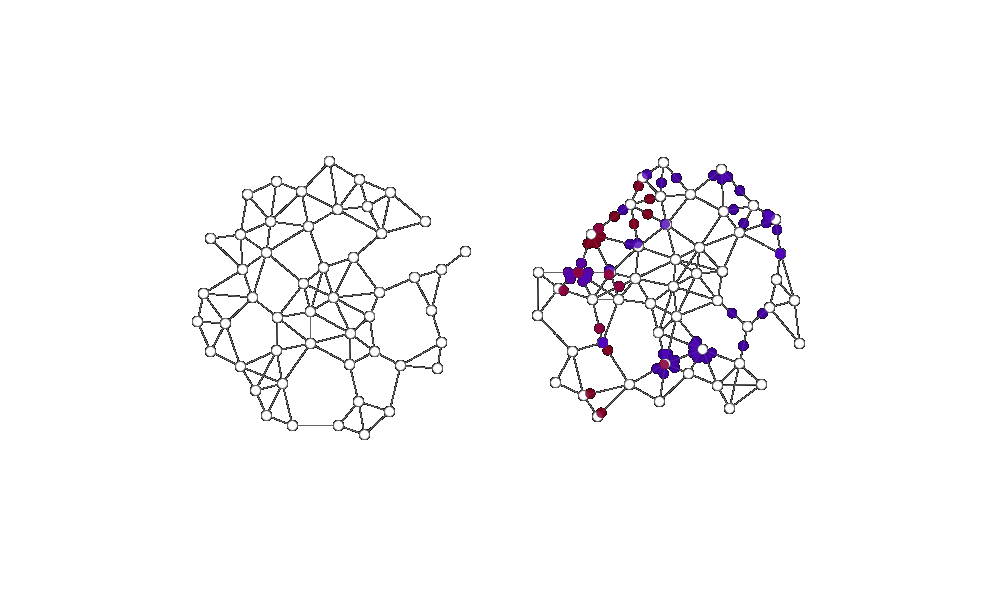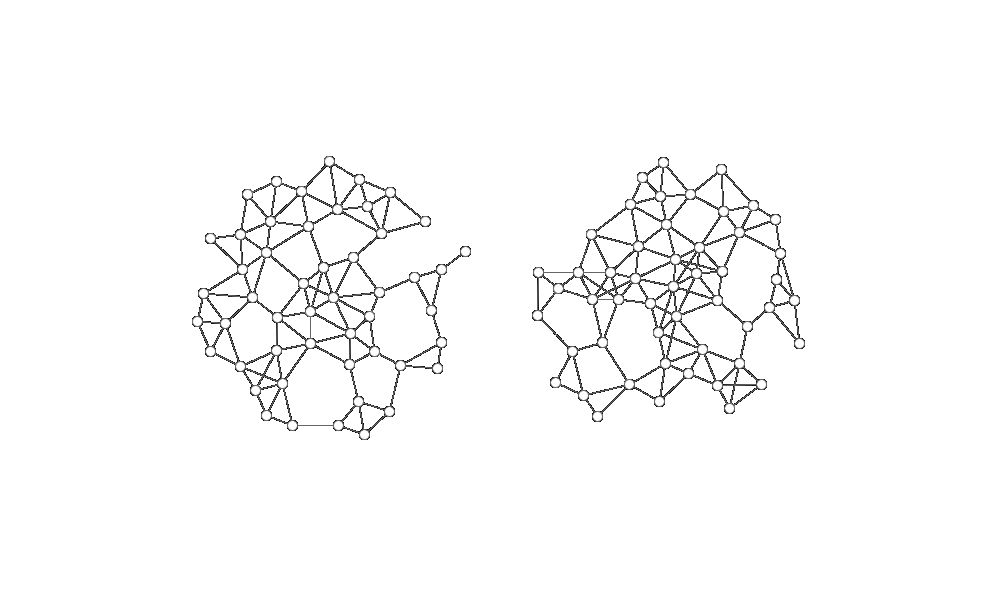
In order to build a robust network, each node will need to have multiple connections spread through the network. Below we see a network where one connection breaks and the network splits into two separate parts. We can avoid this by maintaining multiple connections and trying to spread out our connections to avoid clustering.
We also want to avoid a single node connecting to everyone, they would become a bottleneck for network communication. But a network is very likely to have a dedicated entry node which everyone makes their initial requests through. People could share their own address with their friends as an entry point to the the network, but people tend to just use the default option provided. So how do we create this robust network shape? The easiest solution is to randomly bounce multiple join requests (we’ll call them JOIN_REQs from now on) through the network until enough (however many connections we want to maintain) are accepted. Nodes will accept the JOIN_REQ with a probability equal to one divided by the number of connections they already have plus 1 (plus one to avoid divide by zero errors). This means as nodes gain more connections they are less likely to accept a new connection, while nodes with fewer connections are more likely to accept. This would produce a randomly connected network which is hopefully balanced.
More on joining protocol ideas
If the JOIN_REQ had an equally random chance of being accepted at each hop, then any entry nodes would have much higher chance of being connected to. For example, if everyone enters the network through node A, and every join has a 50% chance of being accepted on each hop, then over 50% of the JOIN_REQs would end up at node A (more then 50% since with multiple hops it can end up back at node A). The chances of even seeing a JOIN_REQ would drop dramatically the farther from node A you are. If you lower the probability of accepting, the average distance to node A would increase, but on average the requests would still center around node A.
Perhaps we use a random walk of length l? We give the JOIN_REQ a hop-count which decreases each hop it makes, then when it reaches zero, it is accepted. What might this result in? It makes sense that the more connections a node has, the more likely our JOIN_REQ has of ending on it (when l is large, the steady state vector can be calculated and large degrees correspond with a higher likelihood of being landed on). That means nodes with many connections are more likely to gain a new connection, increasing their chances again, leading to a positive feedback loop.
You might consider a grid topology where nodes only track up to 4 connections, one for each direction on a compass, then trying to route messages such that a new node would connect to all surrounding nodes (why would you do this? I don’t know, it certainly doesn’t fit our desires, but it would be neat).
What if you require everyone to have exactly d connections, and will not accept any more then that, passing a JOIN_REQ on to someone else? Once the network has d+1 nodes, each will have d connections (every other node), and not a single one will accept any new JOIN_REQs. The network gets stuck. And in fact, it isn’t even always possible for n nodes to have d connections. For example, a graph with 5 nodes, each with 3 connections, is not possible (and in general, regular graphs where n*d is odd do not exist).
Code
We added a default connection point, so if you just type ‘connect’, it will send a JOIN_REQ to the hard-coded default address. But if you want to join a different network, you just type ‘connect some_persons_address.
Establishing connections will be a bit more complicated now. We need to establish a TCP connection in order to send a JOIN_REQ, but that connection shouldn’t give us access to the network because the node hasn’t accepted our JOIN_REQ yet, they may decide to pass it on. If a node does decide to accept, they will send a join acknowledgment (we will now call JOIN_ACK). This means when we are listening for connections we need to be ready to handle two kinds of requests: JOIN_REQs will be temporary connections we immediately throw away, we’ll create a new connection if we decide to accept. Then JOIN_ACKs we will always accept (for now), and so want to maintain the connection and start receiving messages over it.
We need more then just our Message struct now, we need to be able to send JOIN_REQ and JOIN_ACK over connections now. And then our messages need to carry their original sender since we only know the address of the latest node it was announced from, we want to know who originally sent it (we will look at stopping spoofing identity later).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"net"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
)
// we need to track connections in order to send out messages over them
var connections map[net.Conn]bool
// we need to remember messages in order to avoid resending them
// right now we'll just track if we've seen the uniqueID before
var seenPackets map[int]bool
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
connections = make(map[net.Conn]bool)
seenPackets = make(map[int]bool)
go listenForConnections()
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
running := true
for running {
// get text from terminal input
text, err := reader.ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
break
}
text = strings.TrimSpace(text)
// check if the user wants to quit or try to connect to another node, otherwise send out a message
if text == "exit" || text == "quit" {
running = false
} else if arguments := strings.Split(text, " "); arguments[0] == "connect" {
if len(arguments) > 1 {
// enter the network through a user provided address
sendJoinRequest(arguments[1])
} else {
// enter the network through the default address
sendJoinRequest("[::]:55555")
}
} else {
announce(Packet{Type: MESSAGE, Message: text, Origin: myAddress, UniqueID: rand.Int()})
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
package main
import (
"encoding/gob"
"fmt"
"net"
)
func receiveMessage(text string, from string) {
fmt.Printf("%s -> %s\n", from, text)
}
func announce(packet Packet) {
// store packet so we don't repeat it
seenPackets[packet.UniqueID] = true
for connection := range connections {
send(connection, packet)
}
}
func send(connection net.Conn, packet Packet) {
encoder := gob.NewEncoder(connection)
err := encoder.Encode(packet) // writes to tcp connection
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
package main
import (
"encoding/gob"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/rand"
"net"
"os"
"runtime"
"strconv"
"syscall"
)
type PacketType byte
const (
MESSAGE PacketType = iota
JOIN_REQ
JOIN_ACK
)
type Packet struct {
Type PacketType
Message string // text for a message
Origin string // origin of message or JOIN_REQ
UniqueID int // so we can send the same data twice and not have it rejected
}
var myAddress string
func sendJoinRequest(address string) {
fmt.Printf("Sending JOIN_REQ to: %s\n", address)
connection, err := net.Dial("tcp", address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
send(connection, Packet{Type: JOIN_REQ, Origin: myAddress, UniqueID: rand.Int()})
connection.Close()
}
func sendJoinAcknowledge(address string) {
fmt.Printf("Sending JOIN_ACK to accept request from: %s\n", address)
connection, err := net.Dial("tcp", address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
send(connection, Packet{Type: JOIN_ACK, UniqueID: rand.Int()})
go handleConnection(connection)
}
func listenForConnections() {
// start a TCP server to listen for requests on.
// may need to try different ports to find one thats not being used
port := 55555
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":"+strconv.Itoa(port))
for isErrorAddressAlreadyInUse(err) {
port++
listener, err = net.Listen("tcp", ":"+strconv.Itoa(port))
}
if err != nil && !isErrorAddressAlreadyInUse(err) {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
myAddress = listener.Addr().String()
// listen for incoming connection requests
fmt.Printf("Listening for connection requests at %s\n", myAddress)
for {
connection, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
continue
}
// each connection is handled by its own process
go handleNewConnection(connection)
}
}
func handleNewConnection(connection net.Conn) {
connectionName := connection.RemoteAddr().String()
fmt.Printf("Handling new connection: %s\n", connectionName)
// listen for a packet
dec := gob.NewDecoder(connection)
packet := Packet{}
err := dec.Decode(&packet) // blocking until we receive a packet
if err != nil {
// check if client disconnected
if err == io.EOF {
fmt.Printf("New connection disconnected: %s\n", connectionName)
} else {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
// received packet
switch packet.Type {
case JOIN_REQ:
handleJoinRequest(packet)
case JOIN_ACK:
handleJoinAcknowledge(connection)
return // we don't want to close this connection since we may keep it, so return early
default:
// ignore
}
fmt.Printf("Stopped handling new connection: %s\n", connectionName)
connection.Close()
}
func handleJoinRequest(packet Packet) {
// chance of accepting request is inversely proportional to connection count
accepting := rand.Float64() < 1.0/float64(len(connections)+1)
// and make sure not to connect to yourself
accepting = accepting && packet.Origin != myAddress
if accepting {
sendJoinAcknowledge(packet.Origin)
} else {
// change the unique ID so that we could potentially accept the same request if it comes back
packet.UniqueID = rand.Int()
// pass JOIN_REQ to a random connection
for connection := range connections { // ranging over a map is random each time
fmt.Printf("Received JOIN_REQ, passing on to: %s\n", connection.RemoteAddr().String())
send(connection, packet)
break
}
}
}
func handleJoinAcknowledge(connection net.Conn) {
// for now we accept all JOIN_ACKs, we will want to change this later
go handleConnection(connection)
}
func handleConnection(connection net.Conn) {
connectionName := connection.RemoteAddr().String()
fmt.Printf("Handling connection: %s\n", connectionName)
// add connection to our list so we can keep track of it
connections[connection] = true
for {
// listen for a message
dec := gob.NewDecoder(connection)
packet := Packet{}
err := dec.Decode(&packet) // blocking until we receive a message
if err != nil {
// check if client disconnected
if err == io.EOF {
fmt.Printf("Connection disconnected: %s\n", connectionName)
} else {
fmt.Println(err)
}
break
}
// only consider if we have a new packet
if !seenPackets[packet.UniqueID] {
switch packet.Type {
case JOIN_REQ:
go handleJoinRequest(packet)
case MESSAGE:
receiveMessage(packet.Message, packet.Origin) // do something with the message
announce(packet) // pass on
default:
// ignore
}
}
}
fmt.Printf("Stopped handling connection: %s\n", connectionName)
// remove from slice of connections
delete(connections, connection)
connection.Close()
}
// helper function from https://stackoverflow.com/a/65865898
func isErrorAddressAlreadyInUse(err error) bool {
var eOsSyscall *os.SyscallError
if !errors.As(err, &eOsSyscall) {
return false
}
var errErrno syscall.Errno // doesn't need a "*" (ptr) because it's already a ptr (uintptr)
if !errors.As(eOsSyscall, &errErrno) {
return false
}
if errErrno == syscall.EADDRINUSE {
return true
}
const WSAEADDRINUSE = 10048
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" && errErrno == WSAEADDRINUSE {
return true
}
return false
}
Soon we will have a few more files, so lets start using Go’s build command, rather then the run command.
1
go build
Then run the generated executable in three terminals. You should just be able to type connect in the second and third terminal you run, and they should connect to the first. Now end a message from the second terminal, you should see the senders address in everyone’s terminal, not the address of the person who last passed the message on.
Next
We will want to maintain a minimum number of connections. We also will need to alter the joining protocol a bit, since there are some issues with it. But before any of that, we should reorganize our code.